NLRP3
BGE-102: oral CNS-penetrant NLRP3 inhibitor
Lead indications: CV risk, diabetic macular edema
A key driver of metabolic and neuroinflammatory diseases
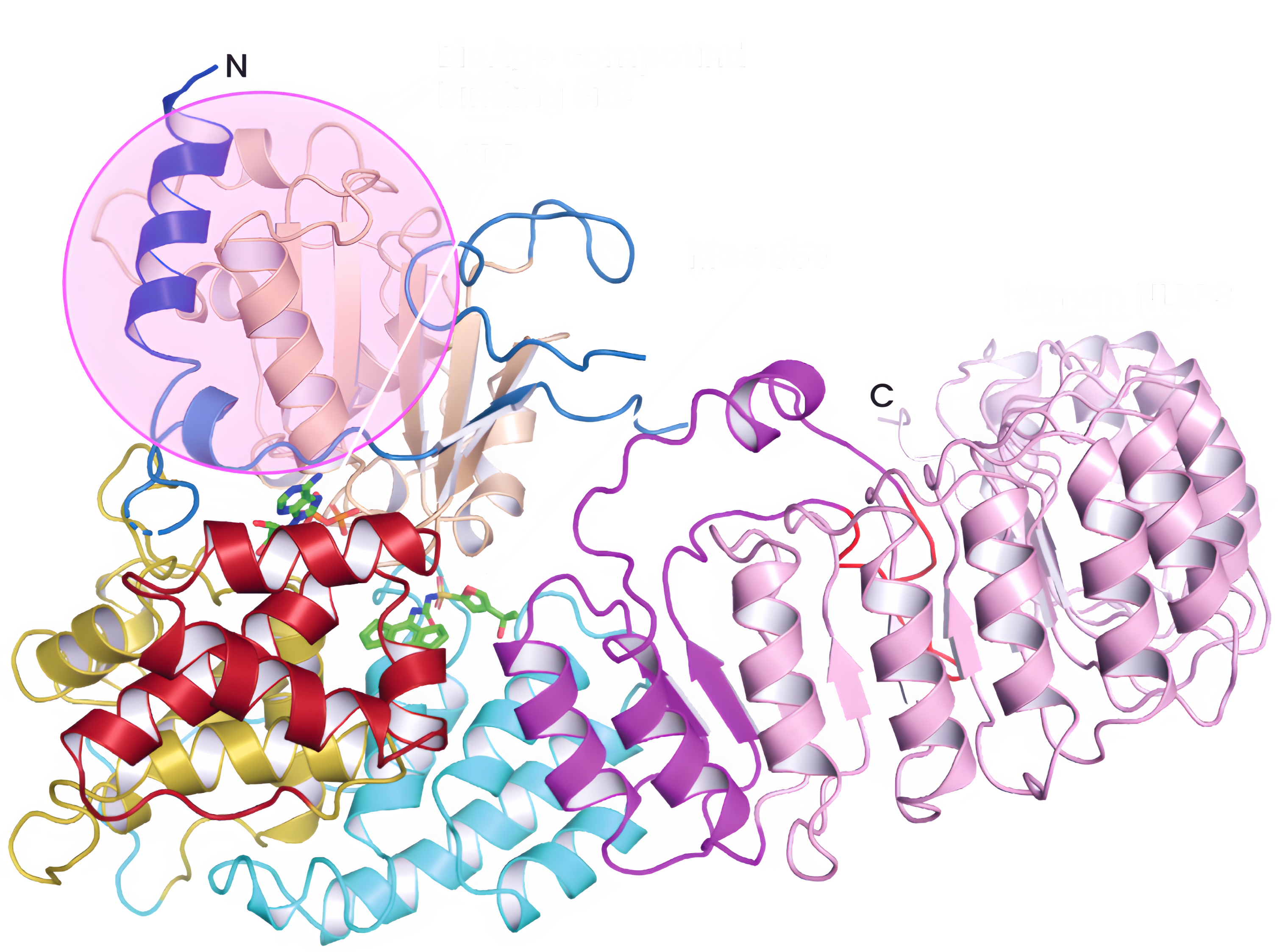
NLRP3 is a critical component of the inflammasome. Chronic inflammasome activation results in inflammation that drives metabolic and neuroinflammatory diseases.
Our lead program, BGE-102, is an oral, potent, and highly brain penetrant NLRP3 inhibitor with a novel structure and binding site.
We anticipate full Phase 1 data in the first half of 2026
Program
Mechanism of Action
Target dosing
Indication
Status
BGE - 102
NLRP3 inhibitor
(CNS penetrant)
(CNS penetrant)
Oral QD
CV risk
Diabetic macular edema
Discoverу
Lead Op
IND-enabling
Ph 1
Ph 2
Ph 3
Discoverу
Lead Op
IND-enabling
Ph 1
Ph 2
Ph 3
We have discovered structurally and mechanistically novel inhibitors that bind in a distinct region of NLRP3